Abstract:A small example of Opencv + tensorflow~
introduce
As deep learning-based object detection has been actively researched, this technique has also been applied to the parking slot detection task 20- 22. The method in 20 generates entrances of. One approach to this problem can be to use a security camera footage to detect the parking occupancy real-time using deep-learning. (Link to complete code at the end) Approach and Architecture. Marking occupancy of a parking slot is a two step process. First we have to determine the location of the parking slot within the field of. To enable parking space perception, we use camera image data collected in various conditions, and deep neural network processing through our ParkNet DNN. To address the geometric diversity in parking shape and orientation, we trained ParkNet to detect parking spaces as four-sided polygons rather than rectangles. As any other Machine Learning algorithms, SVM cannot guarantee 100 percents accuracy in classification. In our parking lots detection, because the neighboring patches have 2 shared parking spaces, confliction may occur when one or both of the two patches are classified into wrong status. 3, we have the results of neighboring. Learning-Deep-Learning PSDet: Efficient and Universal Parking Slot Detection. Tl;dr: Parking slot detection by detecting marking point with a CenterNet-like algorithm. Overall impression. For my future self: Dataset is super important. Your algorithm is only going to evolve to the level your dataset KPI requires it to.
Do you often look around the parking lot to find parking spaces? If your cell phone can tell you exactly where the nearest parking space is, is it very cool? Facts have proved that it is relatively easy to solve this problem based on deep learning and OpenCV. The following GIF images highlight all available parking spaces on the parking lot and show the number of available parking spaces. The key is that the process is real-time.
You can find the code I used in Github repo.
Summary of steps
There are two main steps to build this parking detection model:
1. Check all available parking spaces;
2. Determine whether the parking space is empty or occupied;
Because the camera view is installed, we can use OpenCV to map each parking space once. Once you know the location of each parking space, you can use deep learning to predict whether it is empty or not. I have shared an overview of a high-level step involved on my blog. If you are interested in detailed code, please check out my blog.
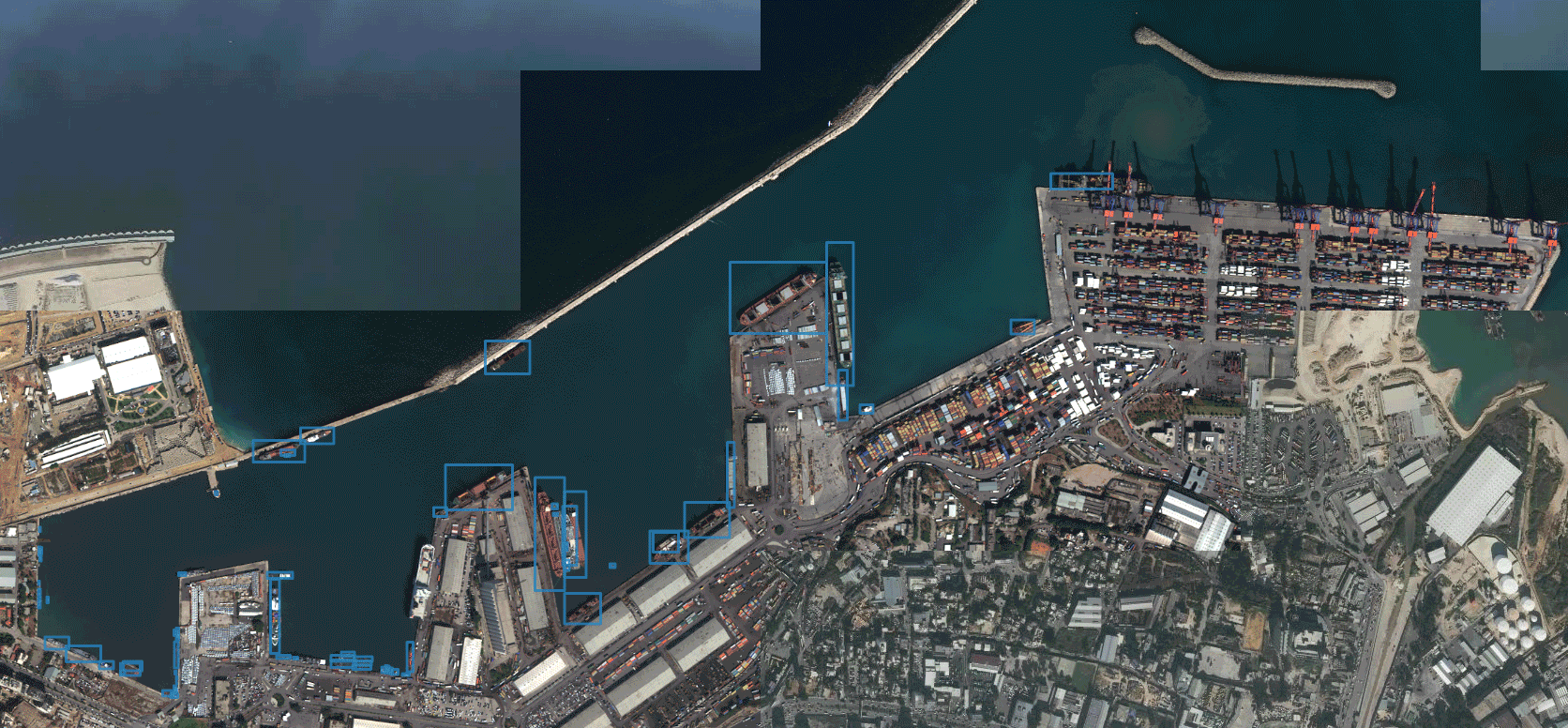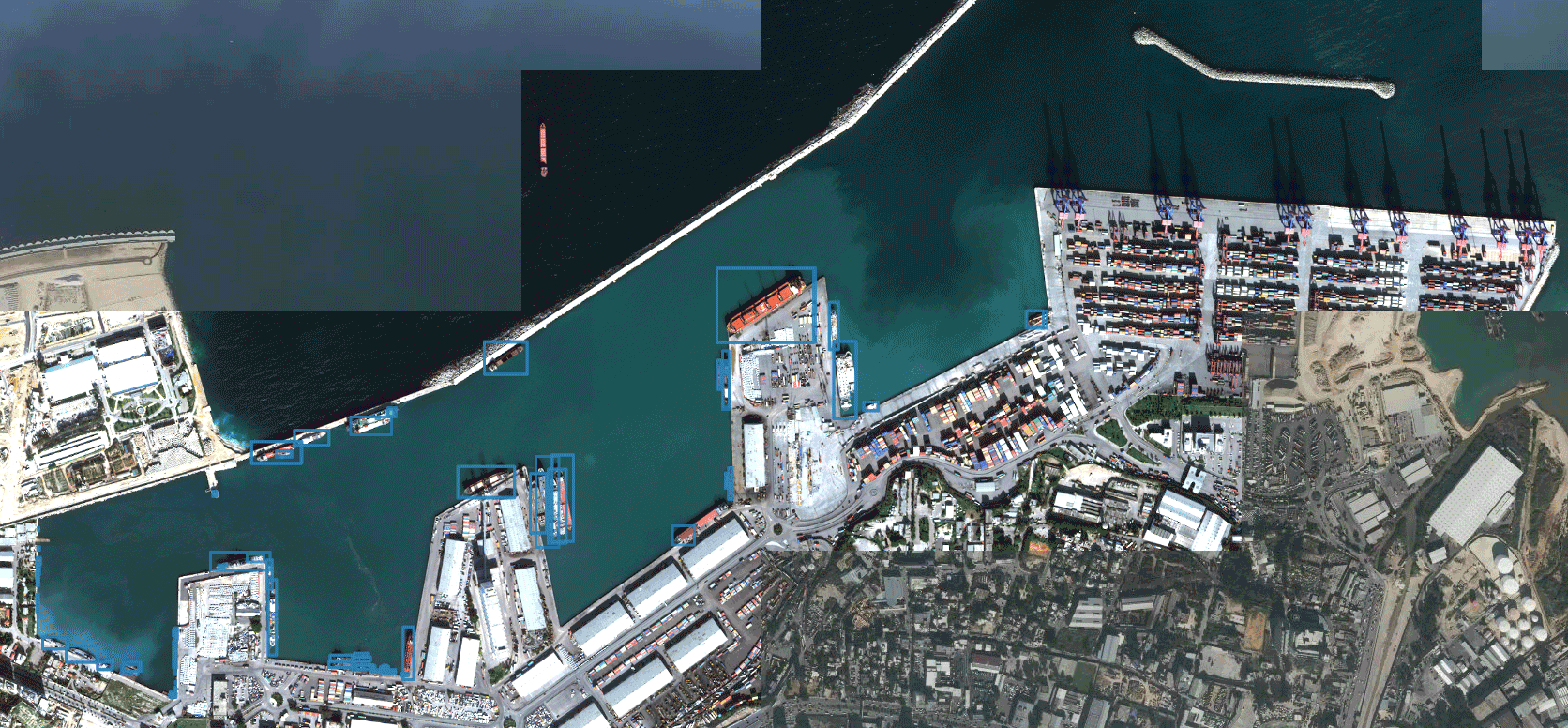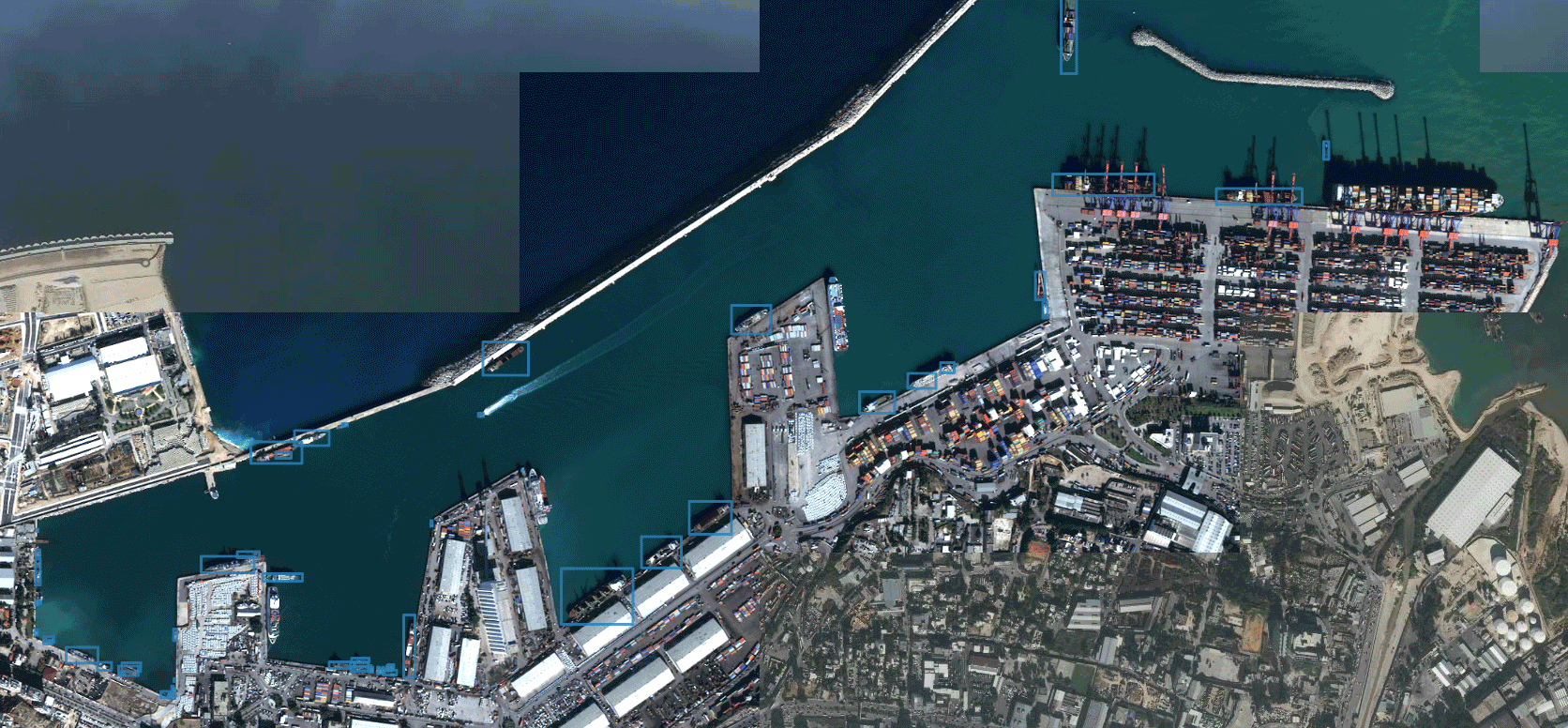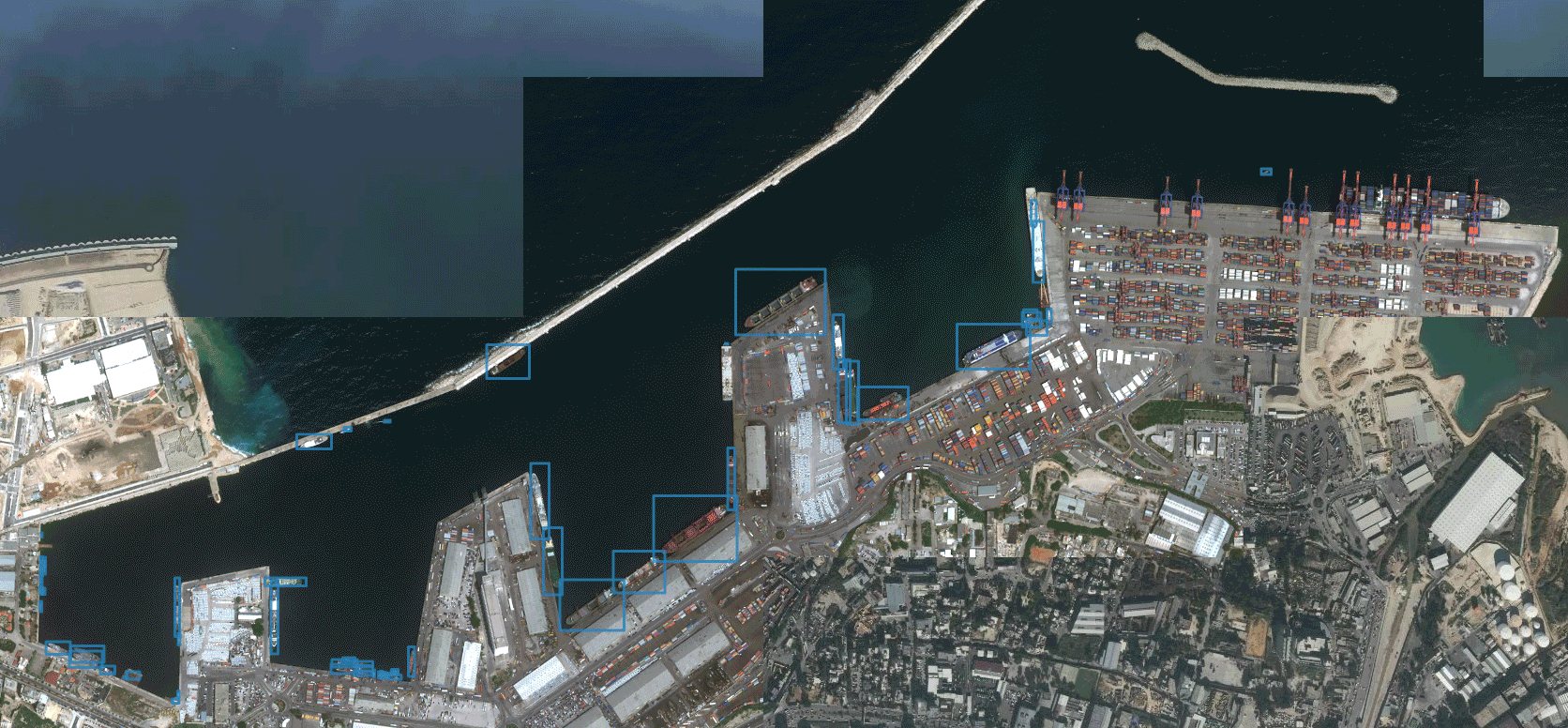
Detection of all available parking spaces
The basic idea of parking space detection is that all parking points are divided by horizontal lines, and the spacing between parking points in a row is roughly equal. Firstly, Canny edge detection is used to obtain the edge image. I’ve covered up the area where I haven’t parked yet. As follows:
Then I did a transformation on the edge image and drew all the lines that it could recognize. I only choose lines with slopes close to zero to isolate horizontal lines. The output of the transformation is as follows:

As you can see, the Hof transform has done quite well in identifying parking lines, but the output is noisy – several stop lines have been detected many times, and some have been omitted. So how do we solve this problem? Then I start with observation and intuition, and use the coordinates returned by the transformation to gather the X coordinates to determine the main parking lane. Clustering logic is used to identify the interval of lane line x coordinates. So you can identify 12 lanes here. As follows:
If all this looks complicated, don’t worry about 5 — I’ve documented the code step by step on github’s jupyter notebook. Now that I know where all the parking lanes are, I can identify each individual parking space by reasonably assuming that all parking spaces are the same size. I observed the results carefully to ensure that the boundary between points was captured as accurately as possible. At last I was able to mark every parking space. As follows:
After locating each parking space, we can assign an ID to each point, save its coordinates in the dictionary and pick it up so that it can be retrieved later. This is possible because with the camera installed, we don’t need to calculate the position of each point in the view over and over again. For more details, please log on to my blog.
Identify whether the parking space is marked or not
Now that we have a map of each parking space, we can determine whether the parking space is occupied in the following ways:
1. Use OpenCV to check whether the pixel color of parking space in video image is the same as that of empty parking space. This is a simple method, but easy to make mistakes. For example, changes in lighting will change the color of an empty parking space, and this method will not work correctly in a day of light changes. If possible, this logic would treat gray cars as empty parking spaces.
2. Use target detection to identify all cars, and then check whether the car’s position overlaps with the parking space. I made an attempt to find that real-time detection model is really difficult to detect small objects, and the detected vehicles are not more than 30%.
3. Using CNN to detect each parking space and predict whether someone is parking, this method has the best effect.
To build a CNN, we need images of parking spaces with and without cars. I extracted the image of each parking space, saved it in the folder, and then grouped the images. I also shared this training folder on Github.
Because there are nearly 550 parking spaces in 1280×720 pixel images, the size of each parking space is only about 15×60 pixels. Below are the images of empty and occupied parking spaces:
However, because occupied parking spaces and empty parking spaces look very different, this should not be a challenging issue for CNN.
However, I only have about 550 pictures of these two classes, so I decided to use the first 10 layers of VGG and add a single soft Max layer to the output of the VGG model for migration learning. You can find the code of this migration learning model here, with an accuracy of 94%. See below:
Now, I combine parking detection with CNN predictor to construct a parking detector with high accuracy.
I also recorded the code running this on the video stream in notebook.
conclusion

I was amazed at how easy it was to combine different tools and use in-depth learning to build practical applications, and I finished this work in two afternoons.
Several other ideas for further exploration:
Parking Slot Detection Deep Learning Software
1. if it is possible to extend the parking detection logic to any parking map that may use deep learning, it is great that OpenCV restrictive use of each use case.
2. The VGG model used by CNN is a weighting model. We want to try a lighter model.
Cloud server 99 yuan group buying! Laxin can also win cash red envelope! Three million waiting for you to split up!
One Click to win the red envelope immediately: http://click.aliyun.com/m/1000019899/
Author: [Direction]
Read the original text
Parking Slot Detection Deep Learning Tool
This article is the original content of Yunqi Community, which can not be reproduced without permission.